The past sentences are very important. Due to the fact, that they allow us to describe actions or past events in history.
The past simple describes actions that happened in a specific moment in the past. On the other hand, the past continuous describes actions that were in progress in the past.
In this topic, you will learn the difference between the past simple and the past continuous in the affirmative, negative and interrogative form, and describe actions that took place in your life. At the same time, you will be able to talk and write about your last holiday and contrast finished actions, mention the actions that were in progress in an specific moment, and finally mention those actions that were happening simultaneously.
By the end of this topic you will:
Use the past simple and past continuous, to describe short stories about your last holiday, to give information in the past and to talk about actions that were in progress.
Contrast the use between Past Simple and Past Continuous the affirmative, negative and interrogative form
The past tenses are essential because they describe actions that took place in our lives.
The past simple is used to talk about finished actions in the past.
Examples:
I traveled to Cancun last summer.
I visited the National Anthropology Museum.
The structure for the past simple (affirmative) is:

I traveled to Cancun last summer
You traveled to Cancun last summer
He traveled to Cancun last summer
She traveled to Cancun last summer
It traveled to Cancun last summer
You traveled to Cancun last summer
We traveled to Cancun last summer
They traveled to Cancun last summer
| Spelling Rules | Base Forms | Past |
|---|---|---|
| Add ed | Work Stay |
Worked Played |
| Just add d if the verb finishes in e | Like | Liked |
| Change y to i after a consonant, add ed | Study | Studied |
| If a one- syllable verb ends in consonant- vowel- consonant. Double the final consonant , add ed | Stop | Stopped |
English club (s.f.) Irregular verbs list [electronic publication].
Consulted 15th, March, 20017.
From: https://www.englishclub.com/vocabulary/irregular-verbs-list.htm
The structure for the past simple (negative) is:
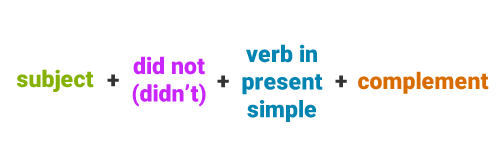
I didn't travel to Cancun last summer
You didn't travel to Cancun last summer
He didn't travel to Cancun last summer
She didn't travel to Cancun last summer
It didn't travel to Cancun last summer
You didn't travel to Cancun last summer
We didn't travel to Cancun last summer
They didn't travel to Cancun last summer
The structure for the past simple (interrogative) is:

Did I travel to Cancun last summer?
Did you travel to Cancun last summer?
Did he travel to Cancun last summer?
Did she travel to Cancun last summer?
Did it travel to Cancun last summer?
Did you travel to Cancun last summer?
Did we travel to Cancun last summer?
Did they travel to Cancun last summer?
Wh- questions are used in the past simple in order to ask for specific information. The structure is:

The past continuous is used to describe an action in progress at a specific moment in the past, or to describe activities that were interrupted by a short action in the past.
Example
I was watching the game last Saturday at ten o’clock.
For the past continuous (affirmative) we use:

| I | was | watching | the game |
| You | were | watching | the game |
| He | was | watching | the game |
| She | was | watching | the game |
| It | was | watching | the game |
| You | were | watching | the game |
| We | were | watching | the game |
| They | were | watching | the game |
Were is used for the plural pronouns and was is used for the singular pronouns.
For the past continuous (negative) we use:

| I | was not | watching | the game |
| You | were not | watching | the game |
| He | was not | watching | the game |
| She | was not | watching | the game |
| It | was not | watching | the game |
| You | were not | watching | the game |
| We | were not | watching | the game |
| They | were not | watching | the game |
For the past continuous (interrogative) we use:

| was | I | watching | the game? |
| were | You | watching | the game? |
| was | He | watching | the game? |
| was | She | watching | the game? |
| was | It | watching | the game? |
| were | You | watching | the game? |
| were | We | watching | the game? |
| were | They | watching | the game? |
The Questions in the past continuous can be answered with short answers.
Wh-questions are used in the past continuous in order to ask for specific information:

• Place
| Example: | Where was (I, He, She, It) going? |
| (I, He, She, It) was going to Chapultepec Park. | |
| Where were (You, We, They) going? | |
| (You, We, They) were going to Chapultepec Park. |
• Specific thing, object
| Example: | What was (I, He, She, It) doing? |
| (I, He, She, It) was eating Mexican food. | |
| What were (You, We, They) doing? | |
| (You, We, They) were eating Mexican food. |
• Time
| Example: | When was (I, He, She, It) going? |
| (I, He, She, It) was going in the morning. | |
| When were (You, We, They) going? | |
| (You, We, They) were going in the morning. |
• Is only used when referring to people
| Example: | Who was (I, He, She, It) going with? |
| (I, He, She, It) was going with my mother. | |
| Who were (You, We, They) going with? | |
| (You, We, They) were going with my mother. |
• Reason, explanation
| Example: | Why was (I, He, She, It) flying by plane? |
| (I, He, She, It) was going with my mother. | |
| Why were (You, We, They) flying by plane? | |
| Because, (You, We, They) were visiting Mexico City. |
We often use the past continuous and the past simple in the same sentence. The action in the past simple is short and usually unexpected. It interrupts the “longer” action which is generally in a past continuous form.
For example:
What were you doing when the plane landed?
I was looking in my bag for my passport when I heard a shout.
We jumped into a car that was waiting for the bus stop.
I was watching TV while my wife was sleeping.
When we have a sentence in past simple and another in past continuous, we often use when and while, but we have to take into consideration the following rules:
| When | When is followed by a sentence in past simple. | When I took the photo, the kids were playing. The kids were playing when I took the photo. |
|---|---|---|
| While | While is followed by a sentence in past continuous. | While I was having dinner, my father arrived. My father arrived while I was having dinner. |
| While is also used when two actions are happening simultaneously. | While I was watching TV my mother was cooking. I was watching TV while my mother was cooking. |
Activity 1
We enjoy sharing our travelling experiences; we talk about them with our family and friends.
Nowadays, this information can be read by people that we don’t even know since we post this information on the web.
Read how Natasha and Bruno’s family spend the last holidays in the blog "My last holidays".My last holiday".
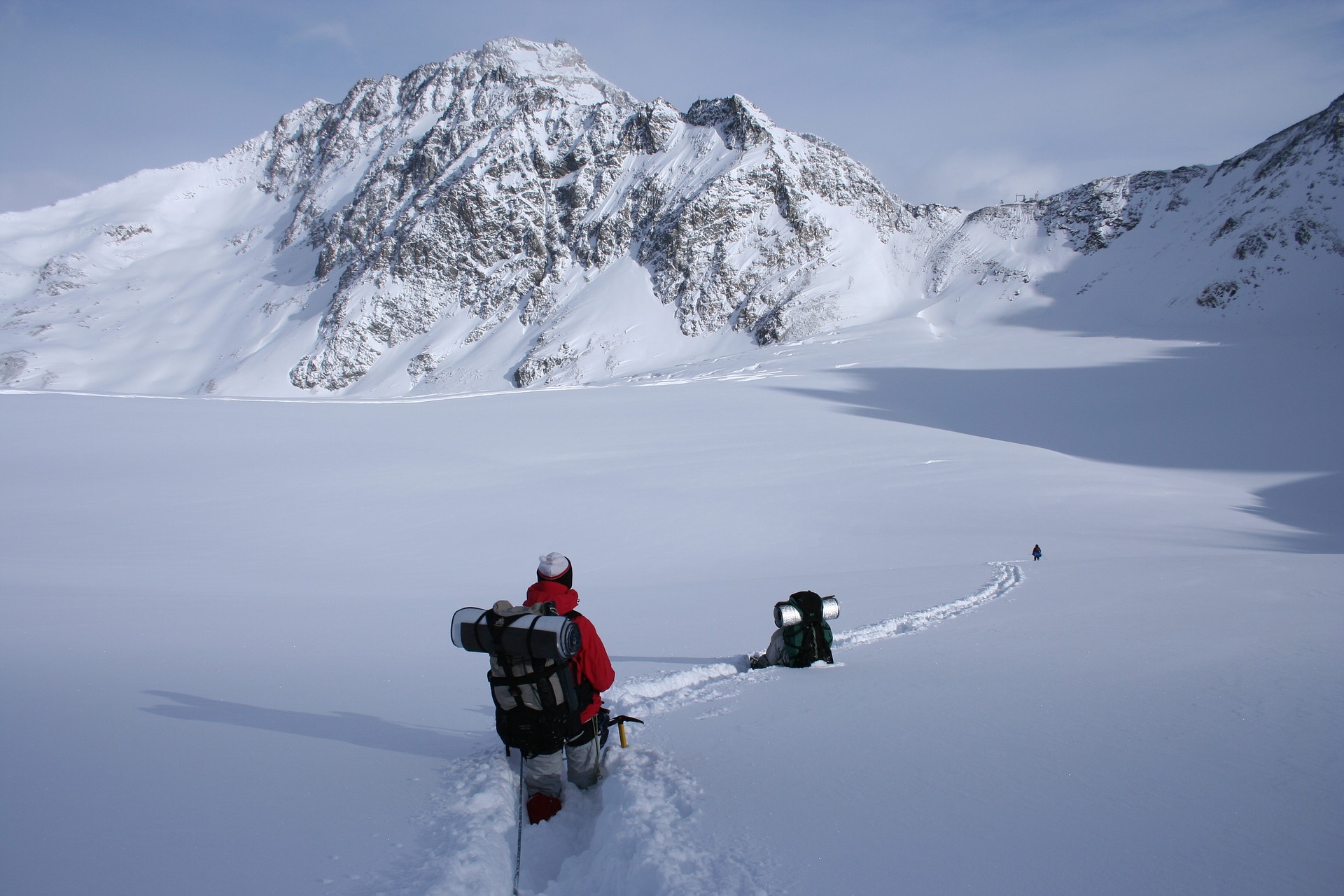

Adam, R. (2007). Alpes [Photography].
Taken from https://goo.gl/LqrjzS
Activity 2
Frank is from Germany and last summer he decided to travel alone and visit Mexico City. After two days, he was so excited that he decided to call his wife to let her know all the details about his trip.
Listen to the following conversation and choose the correct questions. You can listen to the audio several times. However, you will only have one opportunity to answer the exercise correctly.
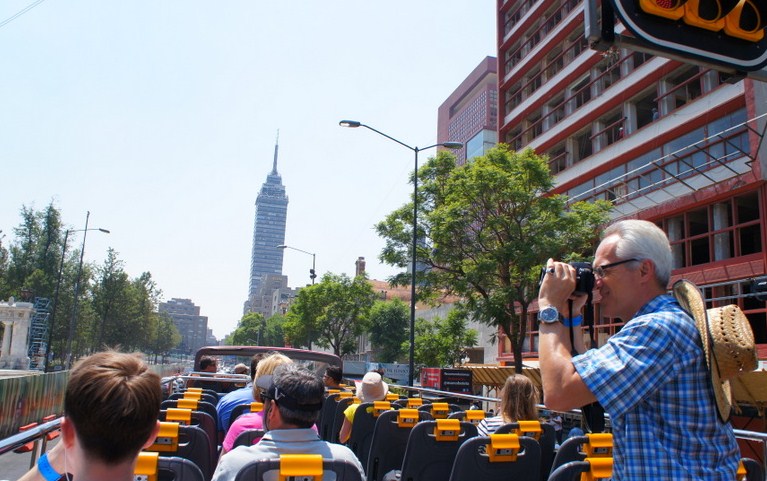

Mexico City Tourism Board (2013). Turibus [Photography].
Taken from https://goo.gl/5lVirN

Activity 3
Photographs are documentary evidence of our life. They help us to remember important moments that will never happen again. Travelling gives us the perfect opportunity to take lots of photos, and like everybody, we always have a favourite.
Choose your favourite photo and write a 100-200 word description by answering the following questions:
Read the following text and use it as an example for your activity.

Before doing your task, do not forget to check the checklist that will be used to evaluate your activity.
Activity 4
We all enjoy talking about our past experiences with our friends and family describing-those moments that were important to us.
Think about the last time you went on a holiday. Read the following questions and answer them. Your answers may be affirmative or negative. Record the questions with their answers and compare your pronunciation with the audio provided.
Before recording, check the rubrics that you will use to self-evaluate your recording.
Allan is talking to you. He is asking you some questions about homework and projects. Order the answers in the following dialogue using when or while.
We have explored the use of when and while in the past simple and past continuous. Now you are ready to identify them in a sentence.
• Oxenden C. & Latham-Koenig C. (1997). American English File. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
• Oxenden C. & Latham-Koenig C. (1997). American English File (2st ed.). Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
• Bolton D. & Goodey N. (1997). English Grammar in Steps. London: Richmond Publishing
• AZAR, B. & HAGEN, S. (2009). Understanding and Using English Grammar (4th ed.). New York USA: Pearson Education.
• MURPHY, R. (2005). English Grammar in Use (3rd ed). Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.